With the rapid development of processors in the past few years, competition in this area between the giants Intel and AMD has intensified, and in the past the competition has always ended quickly to settle in favor of Intel. HOWEVER, AMD WAS ABLE TO RETURN STRONGLY AND CLIMB STEADILY TO THE TOP UNTIL IT SURPASSED INTEL’S SALES OF DESKTOP PROCESSORS AFTER THE RELEASE OF THE SECOND GENERATION RYZEN PROCESSORS.
AMD seems to be planning to take over the top for a long time after announcing the third generation Ryzen processors, whose star will be the great wizard Ryzen 9 3950X, which will be launched by the company next September. The processor is the first processor with 16 kernels.
In this article, we will focus on AMD desktop processors, but for the laptop market, Intel still dominates it very strongly. We explained the differences between them in an earlier article you can read from the following link:
Read also:
Best Value Processors
Never exaggerate when we describe AMD processors as the best value processors. AMD has always surprised us with the low prices of its processors compared to Intel processors. For example, the company has in the past launched the $500 AMD Ryzen 7 1800X processor, which brought similar specifications and performance to intel Core i7 6900K, which at the time cost $1,000.
Of course, if your desktop has a copy of an AMD, you should think carefully about it, so at a lower price you’ll get almost equal performance for Intel processors.
Processor specifications: What do you mean?
When you read about any of the processors, you’ll see a full set of specifications that might confuse you for not understanding what they mean. The most important specifications are:
Cores
By that, we mean the cells inside the processor. Each kernel can work on one task. This means that the higher the number of cells, the more the processor will be able to perform more tasks at the same time and therefore faster. Processors come with two or even four or more nucleations.
Hyper-Threading
It is a technology that exploits resources that are not used in the processor for other software processes. Where the workflow in the processor is organized by the so-called Threads or thread, usually the processor can run a single thread at the same time, but in Hyper Threading technology the processor illusions the operating system as processors and not one, so the operating system will give it two Threads, not one. The technology then distributes processor resources to both threads, the first thread will work and reserve part of the processor’s resources, and the other thread reserves the remaining processor resources. Both threads may need the same resource and then give the supplier the second thread as soon as the first thread is finished.
Clock Speed
Measured in GHz, the number of operations per second can be performed by the CPU. The higher number is the best, but this specification is not the only one that determines the processor speed.
Turbo Boost
Temporarily, it automatically increases the speed of the clock from its primary frequency to a higher frequency to complete the task more quickly. The default frequency is mentioned as “processor frequency” while the highest frequency it can reach is listed as “turbo frequency” or “speed after booster.”
Cache
A small memory directly linked to the CPU, this memory stores information frequently used to speed up repetitive tasks. Most CPUs have a cache of between 1 and 4 MB and can reach up to 12 MB. Of course, the higher the number, the better the processor.
You can review our custom cache article:
TDP (Thermal Design Power)
The amount of watt power used by the CPU. More watt means better performance, but higher temperatures and increased energy consumption.
AMD series
Here are some of the famous AMD strings.
AMD A Series
This series of processors consists of three sub-families, dual-core A6 processors, quad-core A8 processors and the most powerful quad-core A8 processors than its predecessor. This series is suitable for light use such as surfing the internet, watching video, text processors and light hussa tasks. These processors have a built-in graphical processor.
Examples include the AMD A10 9700 kernel quadrupled processor, which comes at 3.5 GHz and a top speed after boostering up to 3.8 GHz, comes with 2MB of cache memory, 4 threads and 65W power consumption and integrated with radeon R7 graphical processor.
Ryzan Series
Just like Intel’s popular Core i series of processors. Ryzen processors are common from AMD and can be considered roughly equivalent to Intel Core i processors.
Ryzan 3
The outstanding therapist of the Ryzen family. This family offers similar performance but is slightly lower than Intel Core i3. It has enough processing power for everyday computing tasks and can handle fairly intense tasks. It’s also cheaper than Intel Core i3 processors. It is a quad-core.
Examples include the AMD Ryzen 3 2200G kernel-vendor processor, which comes at 3.5 GHz and a top speed after boostering up to 3.7 GHz, and comes with 4 MB of cache memory, 4 threads and 65W power consumption.
Ryzan 5
Ryzen’s mid-range processor family. Come either quad-core or hexagonal processors. Ryzen 5 processors have higher speeds that deliver enough performance to handle fairly intense tasks. This family is the direct competition for Intel Core i5 processors.
Examples include the AMD Ryzen 5 2600X Sadie Kernel processor, which comes at 3.6 GHz and a top speed after boostering up to 4.2 GHz, and comes with 16 MB of cache memory, 12 threads and 95 W power consumption.
Ryzan 7
It is the family of high-performance processors from Ryzen, the rival family of Intel Core i7 processors. Ryzen 7 processors come either quad-core, hexagonal or octa-core. Capable of handling intensive computing tasks much better than Ryzen 5 processors.
Examples include the AMD Ryzen 7 2700X octa-core processor, which comes at 3.7 GHz and a top speed after boostering up to 4.3 GHz, and comes with 16 MB of cache memory, 16 threads and 105 W power consumption.
Ryzan 9
Is the new family of Ryzen. It has very high speeds. Intel Core i9’s main competitor, which can handle highly intensive computing tasks and applications, has multiple cores of up to 16 cores, which will go on the market in September.
Examples include the AMD Ryzen 9 3950X 16-core processor, which comes at 3.5 GHz and a top speed after boostering of up to 4.7 GHz, comes with 64 MB of cache memory, 32 threads and 105W power consumption and integrated with a Radeon R7 graphical processor.
Ryzan Threadrippers
Are multi-core super-performing processors. Designed to handle a lot of multitasking and applications that require a lot of complex calculations.
Examples include the 32-core AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX, which comes at 3.0 GHz and a top speed after boostering of up to 4.2 GHz, with 64 MB of cache memory, 64 threads and 250W power consumption and integrated with radeon R7 graphical processor.
Athlon PRO and Ryzen PRO
AMD PRO processors are designed for business, providing reliability, security and high performance to meet the intensive business requirements that organizations and businesses focus on. All AMD PRO processors across the product range provide quality and reliability at a business level to help ensure that platforms work longer and support non-standard management capabilities to enable increased management flexibility in a multi-vendor customer environment at a business-friendly price. In addition, AMD’s GuardMI technology enables the latest device protection technology from start-up to shutdown, helping to protect against increased threats.
Examples include athlon PRO 200GE and Ryzen 7 PRO 2700X processors.
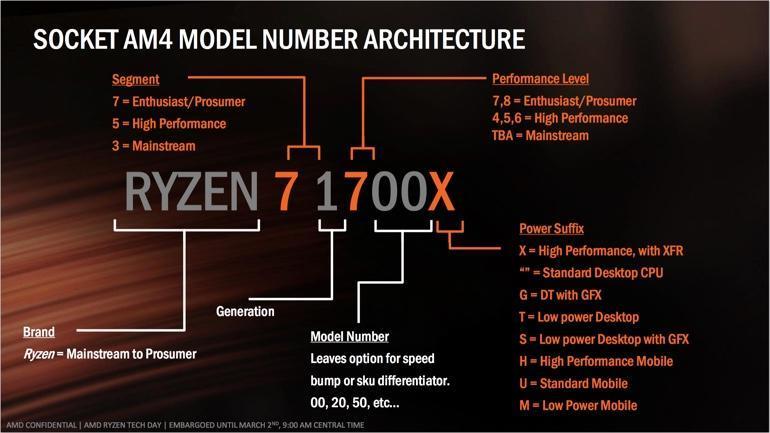
How do you read the Ryzan processor model and what do the symbols in it mean?
When you look at the processor model in the spec sheet, you’ll notice that the processor has a confusing combination of numbers and burns. Don’t worry.
Brand
This part is intended for the processor’s brand and will be either “Ryzen” and “A” or any other AMD family.
Brand Modifier
After the brand, it’s the place for the family status of the brand, which is often 3, 5, 7, or 9.
Gen Indicator
The first number after the brand category is the generation number. Currently the latest generation is the third, so our latest CPU so far has the number 3 in this box.
Performance level and Model number
After that, you’ll probably see a combination of two or three digits. The first processor strength number indicates the subsequent numbers to SKU.
Power Suffix
In the end, you may see one character, which refers to the processor’s usage line and gives an impression of its power.
- The letter “G” indicates that the Ryzen processor has the AMD Radeon RX Vega graphics card. This is also true in the Intel Core I series. Intel Processors with subsequent G-addresses contain the AMD Radeon RX Vega graphics card.
- The “X” also refers to high performance. Ryzen X-up processors have the highest 24-hour speed and power consumption and are the fastest performing. These Ryzen chips are desktop processors. X subsequent processors have the advantage of extending the frequency band (XFR). This allows the processor to enhance its performance above normal limits.
- The “U” refers to very low power. A thin and light laptop that comes with Ryzen’s U-suffix processors, the Ryzen Suffix U processors feature less speed around the clock and consume less power. It also produces much less heat than other processors. Thin laptops benefit from this because the shape factor and the thermals don’t get rid of heat easily.
- The “H” refers to high performance. Ryzen H processors have higher time and power consumption speeds, which translates into higher performance. They are usually found in large laptops because of the best cooling system you provide.
- There’s no letter. Ryzen processors without suffix are desktop processors.
Example
We’ll give an example of amd Ryzen 5 2600X.
- 2 in 2600X is the generation processor AMD Ryzen, in our example this second generation processor. The larger the generation, the more performing it is than the previous generation.
- 6 in 2600X is the performance level. Numbers 4, 5 and 6 are high-performance processors. 7 and 8 are for video editing, music production and CAD work at the enterprise level, this processor is suitable for heavy engineering programs and professional animation.
- 00 in 2600X is a model number or a number (SKU).
- The “X” suffix we’ve already talked about indicates that it’s a high-performance processor capability. It also has an Extended Frequency Range (XFR) feature that allows it to increase its performance above its limits.
Ryzen 3G Processors
Through Computex 2019 AMD unveiled the third generation Ryzen processors, the 3G is manufactured with 7 nm technology and supports up to 12 kernels and 24 threads. These processors are built on zen 2 architecture and are compatible with the current AM4 motherboards. Ryzen 9 3900X is the leading processor of these processors and works with 12 kernels to be the first video game-oriented processor with this number of nuclei.
The cash memory in this processor is 70MB, and the power consumption is estimated at only 105 watts. The processor runs at 3.8 GHz and can reach 4.6 GHz using payment technology, and will launch on July 7th at $499
Intel vs. AMD
Performance and speed break
- If you want a processor to play games but your budget is limited, there will be a higher cost to purchase a processor with a built-in GPU, although many Intel processors come with a built-in graphics processor that’s not powerful enough to play games. AMD has decided to change the whole thing with the launch of the Ryzen 5 2400G processor, which comes in built-in with a dedicated Vega 11 graphics processor. So if you want a gaming processor with a low budget, you should think about AMD products because they offer the best price performance.
- If we look at Intel Core i9 and AMD Threadripper, which are the most advanced and quality processors, Intel takes precedence when it comes to performance.
- If you’re looking for the best processor performance when you raise or break the operating frequency, Intel is your best bet. This is related to technologies such as intel’s most advanced hyperthreading and turbo-boost. Although AMD has similar techniques especially with Ryzen processors, the ball is still in Intel’s court at this time.
Which game wizard is better?
Although it’s relative to the design of each game and each processor, Intel processors are well designed with games in mind, which is reflected in overall performance.
Despite AMD’s attempts at its processors’ performance when playing games in Ryzen processors, many games are designed to get the most out of Intel processors via DirectX11 and 12.
But for gaming platforms, AMD is dominant, with both Xbox One and PlayStation 4 devices operated by AMD processors due to the company’s APU (Accelerated Processing Unit).
Better built-in graphics processor
This question is easy to answer as AMD has many custom graphics cards on the market while Intel doesn’t make custom graphics cards. In this area, AMD certainly excels as Intel has decided to use AMD graphics cards with its H-Series laptop processors.
Price
Although the two companies have many excellent processors, AMD offers the best performance for every dollar you pay for a CPU. For AMD you’ll get the best value for every dollar you pay.
In the end.
That’s all about AMD computer processors. You now have the experience to see if your COMPUTER with the AMD chip has enough performance to meet your needs or what is the best option.







تعليق واحد