RAM is a short-range memory inside your PC, used by your computer or phone to temporarily store the software and data you are currently using until you close it. Of course, everyone knows that the more ram space available, the better, you may now consider buying a new RAM for your computer.
Shopping for a new RAM for your computer can be confusing. What is the difference between DDR3 and DDR4? DIMM and SO-DIMM? Is there a difference between DRR3-1600 and PC3-12800? What do we mean by Timing and Latency and what is ECC?
What is RAM?
Random Access Memory, known as RAM, is a cache memory that acts as a medium in the CPU that is described as super-fast, and between a large volume that may be either a hard drive (HDD) or a hard drive (SSD) that is described as large and slow-speed — compared to cache – your RAM system uses to store working parts of the operating system and parts of the active applications and data you use.
To make it easier to photograph your computer as if it were your personal office, the hard drive will be like the closet where you keep your important files, ram will be like the desktop you sit in front of and represent your work area that contains the documents you are trying to accomplish, but the cache will be the part where you put the document you are working on at the moment which is the small part of the desktop where you put the document or file and start working on it.
Imagine if we brought a bigger office to work, you could bring more documents from the closet and put them on the desktop to work on without the office becoming messy and untidy. This is similar to the fact that the more RAM space on your computer, the more things (programs, apps, files) you can access at the same time while working and quickly.
But unlike your office, RAM can’t keep files inside them permanently, once the computer is turned off all the data on it will be deleted, for example when you’re working on Excel at this time all the data you’re working on is stored on RAM and you know what happens if the power goes out of your computer before you save that data on the hard drive. You’ll lose all the data you’ve written so once the power is turned off, the RAM will clear everything, so we always recommend that after you finish working on any document in your office, return it to the locker to save it so that the cleaner doesn’t accidentally throw it away.
When we mention RAM, we always mean SDRAM!
When people mention the term RAM, they usually mean synchronous dynamic RAM, known briefly as SDRAM. For most desktops and laptops, ram is a stick-like part that you can insert or remove from the motherboard.
Unfortunately, there are some companies that are concerned with the manufacture of ultra-thin and light laptops that tend to make ram welded directly to the motherboard and cannot be removed or changed to save space. But all this is at the expense of a computer-capable upgrade and easy fix.
Don’t confuse SDRAM with SRAM, which means static RAM. Static RAM is the type used in the CPU cache, which is much faster but limited in capacity, making it unsuitable as an alternative to SDRAM. Don’t worry about the SRAM it’s very rare as a user to see it where you’re using it.
You can review our custom cache article:
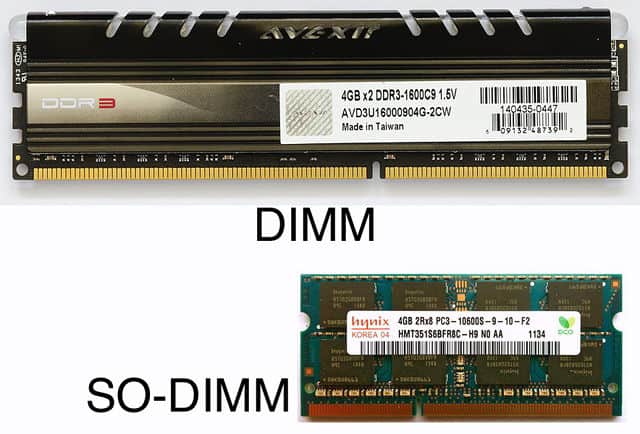

RAM forms
RAM comes in two different criteria for the format: the first is the DIMM (two-way integrated memory unit) found in desktops and servers. The second criterion is so-dimm (Small Outline DIMM) found in laptops and other small-sized computers.
Although the RAM forms use the same technology and work functionally in exactly the same way, you can’t switch between them, you can’t put a DIMM ram in the SO-DIMM slot, and vice versa (each shape has a slot type in the motherboard that’s right for it).
When you buy a new RAM for your computer, the first thing you should know is the standard shape your computer adopts for RAM.
What does DDR mean?
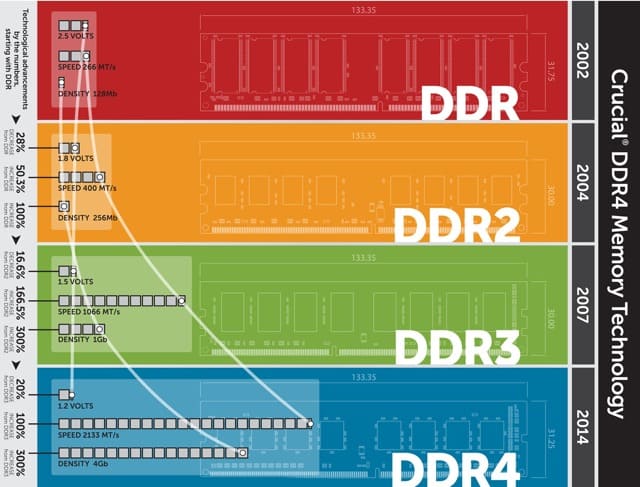
The double data rate known as The Telly (DDR). This means that DDR can do two transfers during a single time pulse. In the past, we had single Data Rate or SDR, which could only perform one ifl during a single time pulse. The newest types of DDR are updated versions of the same technology so you’ll find ram units available on the market carrying different symbols DDR, DDR2, DDR3, etc.
While all RAM generations are exactly the same size and physical shape, they are incompatible. You can’t use DDR3 ram on the motherboard that only supports DDR2. Similarly, DDR3 does not comply with the DDR4 slot. To prevent any confusion, each generation of RAM has small pieces of installation nails in different locations. This means that you cannot install the wrong type even if you try to prevent the motherboard from being accidentally damaged if you purchase the wrong type.
Read also:
DDR2
DDR2 is the oldest generation of RAM, rarely encountered today. This type has 240 copper plug (200 for SO-DIMM). You can still buy this type in limited quantities for the purposes of upgrading older devices. Otherwise ddr2 is outdated.
DDR3
The DDR3 generation was released in 2007. Although this type was officially replaced by DDR4 in 2014, you’ll find plenty of computers using this type. But why? Computers that support DDR4 did not appear until 2016, two years after the launch of The DDR4. Furthermore, DDR3 SDRAM supports a wide range of CPU generations from the LGA1366 intel socket to LGA11151, plus AM3/AM3+ and FM1/2/2+ from AMD.
DDR3 RAM has the same number of conductive coppers as ddr2. However, it works less hard and has a higher speed so you can’t use DDR3 in a DDR2 support panel. The DDR3 SO-DIMM also contains 204 delivered coppers versus 200 delivered coppers in DDR2.
DDR4
The DDR4 generation reached the market in 2014, yet it has not been able to spread strongly in the RAM market for a long time, mainly because RAM prices have risen dramatically, which has prevented many people from thinking about upgrading. But as prices drop, many users have begun the upgrade process, especially since generations of new AMD and Intel processors all use ddr4 exclusively. This means that if you want to upgrade to a more powerful CPU, you need a new mother board and a new RAM as well.
The DDR4 is working on a 1.2-volt voltage less than the 1.5-volt voltage used in The DDR3, with the number of conductive coppers increasing to 288.
DDR5
DDR5 generation decals are scheduled to reach consumer markets this year. But given how long it usually takes for a new generation of RAM to spread, we expect to hear more about it in 2020. The manufacturer of sk Hynix expects DDR5 to make up 25% of the market in 2020 and 44% in 2021.
The DDR5 will come with 288 connecting coppers but will work at 1.1 volts. DDR5 performance is expected to be twice as fast as DDR4. But the problem at first will be the price is too high when it is launched. If you’re considering buying a new mother board, don’t give a damn about the DDR5. Because they are not available and you will need some time.
RAM specifications
Well, we hope you understand everything we said about SDRAM, DIMM and DDR. But you may be asking, what about the other long strings of numbers in the RAM specification sheet? What do you mean? What does RAM measure? What about ECC and Swap? Here are the terms for ram specifications you need to know.
The united states of The United States of The United States of The United States of The United States of
You may have seen ram indicated by two series of numbers similar to the DDR3-1600 and PC3-12800. The words DDR and PC with the number immediately after them and before the signal (-) refer to the memory generation, PC2 is the same as DDR2 and PC3 is the same as DDR3, and so on.
As for the numbers, the numbers after the generation type associated with the word DDR indicate the rate of transfers per second and are measured in a mega-transport unit per second (MT/s)! That is, the number 1600 in DDR3-1600 means that memory has a transfer speed of 1600MT/s. As for the numbers associated after the word PC and generation number, theoretical bandwidth is measured in MB/s, i.e. the memory above with PC3-12800 specifications operates on a frequency band of 12800MB/s.
The ram’s operating frequency can be raised, just as you can raise the CPU or graphics card frequency (breaking speed). Higher operating frequency increases RAM bandwidth. Manufacturers sometimes sell pre-raised repeats, but you can turn up the operating frequency yourself. Just make sure that the motherboard supports a higher running speed.
You may be wondering if you can mix RAM units that have different speeds in computers that have more than one RAM portal. The answer is yes, you can, but it will all run at slower RAM frequency speeds. If you want to use RAM faster, don’t mix it with older and slower units. In theory, you can mix more than one ram brand, but this is not recommended. You’ll get a greater chance of facing the famous “Blue Death Screen” holidays or other random crashes when blending branded RAM or different speeds.

Timing and Latency
You will sometimes see RAM units with a series of numbers similar to 9-10-9-27. These numbers are referred to as timing. RAM Timing is a measure of ram unit performance per second. The lower the numbers, the faster the RAM responds to requests.
The first number 9 in the previous example refers to the CAS response time, which is the number of cycles required by the data required by the memory controller to become available on the data conduction copper.
You may notice that DDR3-generation RAM generally contains higher timing numbers than DDR2, and that DDR4-generation memory generally has higher timing numbers than DDR3. However, the DDR4 is faster than the DDR3 which is faster than the DDR2. Is that weird?
The lowest running speed of DDR3 IS 533 MHz, which means a periodic time of 1/533 million or 1.87 nm. With a CAS response time equal to 7 cycles, the total latency is 1.87 x 7 = 13.09 nanoseconds.
The lowest running speed for RAM (DDR4) is 800 MHz, which means a periodic time of 1/800,000,000 seconds or 1.25 nanoseconds. Even if this cas generation had a higher example of 9 cycles of total transition it would be 1.25 x 9 = 11.25 nanoseconds. That’s why the DDR4 generation is faster than DDR3 even though it has a higher CAS response time!
For most people, ram capacity factor is more important and preferable to ram frequency (speed) and response time. Everyone would prefer 16GB of DDR4-1600 RAM than the 8GB DDR4-2400. Ram speed and response criteria are often the last points of interest.
Ecc
ECC RAM error correction software is a type of computer data storage that can detect and correct most types of internal data corruption. ECC memory is used in computers where no data damage can be tolerated under any circumstances, such as scientific or financial computers.
Typically, ECC memory maintains a memory system that is immune to single-bit errors: the data read from each word is always the same as the data written, but if one or more stored bits are turned into the wrong state. Most types of memories cannot detect errors, but ECC can detect errors.
Consumer-oriented panels and processors do not usually support ECC-compliant RAM. Unless you’re building a computer that specifically requires the presence of ECC RAM, stay away from it and don’t care about it.
How much RAM do you need?
In the past 640 kb of memory was enough for anyone! But in a world where smartphones are made with at least 4GB of memory, these capacities of memory have already become nothing for the average user. Especially with programs like Google Chrome that are equal to most of your ram space so you can work quickly on them.
In the following picture there is a graph showing how the average RAM capacity on computers increases as we progress in time.
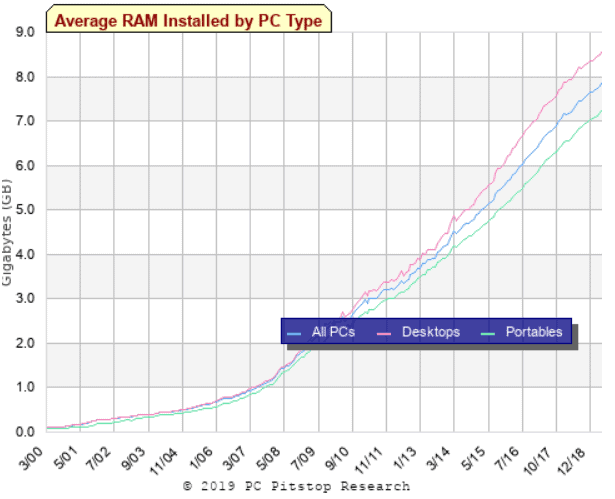
For most people, 4GB is the minimum RAM you need for a computer for public use. Operating systems have different specifications, for example, you can run Windows 10 on only 1GB RAM, but you’ll find a slow user experience. On the contrary, many Linux distributions work well with less RAM.
If you find yourself having to open six Word documents at the same time, of course with 4GB, you won’t be able to do so until you close the 60 tabs you’re browsing on Google Chrome, unless you have at least 8GB OF RAM, you can open them next to 60 tabs in Chrome.
For 16GB of memory, it should be almost enough for everything. Very few people need 32GB RAM only those who work on professional animation programs, heavy drawing software and montage programming in the same computer.
That’s it.
You now know the difference between RAM DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4. You can learn DIMM from SO-DIMM, and learn how to get RAM at faster transfer rates and higher bandwidth.You’re now an expert on that.
Of course, the frequency of work (work speed) and responsiveness play a role, but capacity is the main thing. When you’re in doubt, remember this sentence: “More RAM is better than a higher-speed memory,” unless you have to choose between two same-capacity ones, then make sure you choose the highest speed.




إترك رد