Motherboard is the most important element in your computer. If the motherboard crashes or one of its connections is disabled, all components of your computer will be disabled. Unfortunately, i don’t know. Motherboards look like a mysterious and magical part for those who are not tech enthusiasts.
With so many parts, parts and components, discovering the purpose of each of their components may seem like brain surgery. Read on for a simple and basic comprehensive guide to your motherboard!
Overview
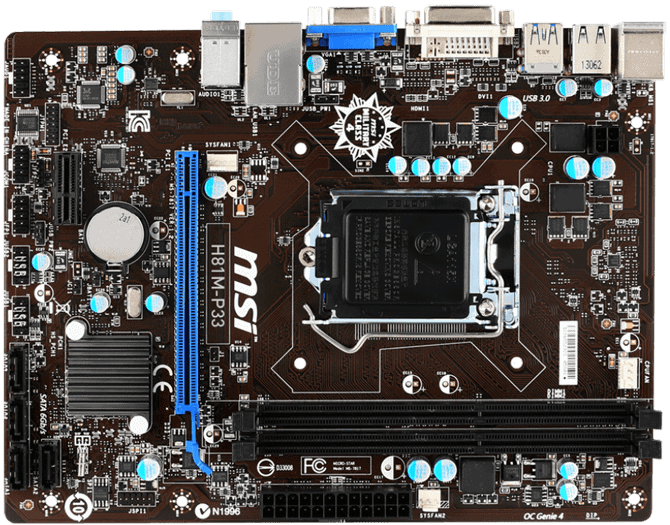
To give the simple components of the motherboard the most expensive image, an image of an MSI H81-P33 panel.
Read also:
Although there are more complex components of the motherboard that allow users to install more parts, in the example above we will show the basic components in all panels. At first, we must distinguish between three types of compositions in the motherboard:
- Slots: Incisions in the form of cracks resulting in the absorption of some components. The main openings on the motherboard are: AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port), PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) and RAM (Randon Access Memory).
- Sockets: Any plugs, the plugs allow users to install some parts directly into the motherboard. as a CPU socket.
- Connections: Connections provide a way to transfer power through your power source to the iron. These links are often links to pin-like ends, some of which are placed in closed special sockets (e.g. ATX sockets), while others are exposed.
Although the design of specific motherboard models includes more compositions than mentioned above, the ones mentioned are the main formulations of consumer-level painting.
CPU socket
The CPU socket is similar to the plug of any electrical device you have, for example. The power socket provides a way to connect it to the electrical grid, giving it the power it needs to work. Its CPU socket provides an incubator mounted on top to provide power and provides a cpu to connect to the rest of your computer components.
Plugs come in two types: LGA and PGA. LGA and PGA can be understood as two opposite-type sockets. LGA consists of a socket with connecting heads that the processor puts on. On the contrary, in PGA sockets, the plug heads are mounted on the processor and inserted into holes on the appropriate socket.
Read also:
- How do you know the motherboard model on your computer? What is CPU Socket and what is the difference in its types?
- A comprehensive comparison of different laptop processors and differences, how do you choose the right processor for your computer and your usage?
- Everything you need to know about AMD processors, the complete guide to the company’s best value processors!
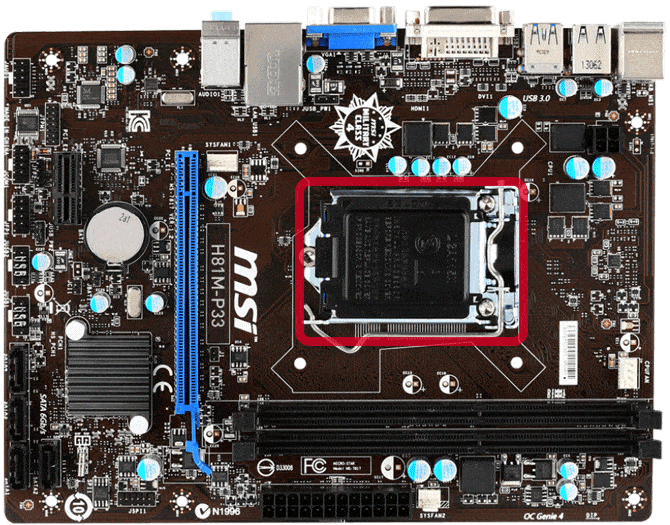
There are also different versions of sockets of each type, each different from the other in terms of the type of processors it can accommodate. The motherboard will have high quality or more expensive high-quality sockets.

Installing the CPU in the socket is simple, just putting the CPU over the socket taking into account the correct direction (as shown on the processor via a small arrow pointer) and pressing the CPU to contact the socket using the contact lever.
The following video shows how to install the processor.
DIMM Slots
DIMM slots (Dial Inline Memory Module) accommodate RAM units. They are usually parallel to the rear power connectors of the mother board.
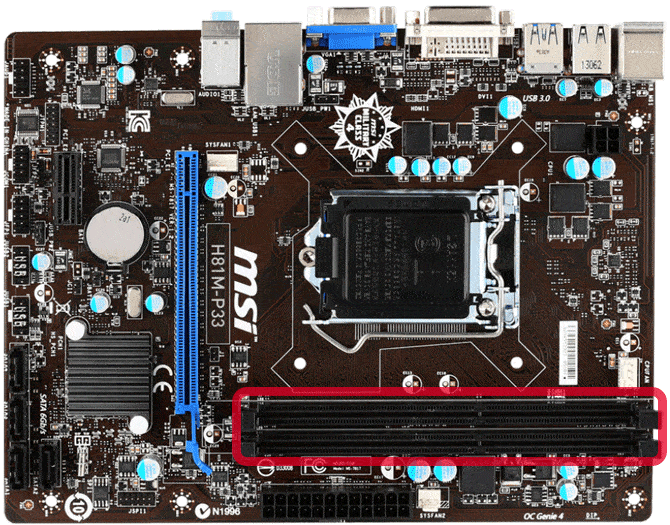
DIMMs slots vary by the number of connecting teeth, for example, SDRAM slots have 168 years and DDR SDRAM slots have 184 years.
Read also:

To properly install the slots, open the two small levers on each side of the DIMM slot and press down the RAM until it settles in place.
PCI Slots
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots accommodate components such as graphics card and audio cards. Modern homeboards mainly use different PCIe versions of PCI Express. The latest PCIe standard is PCIe 4.0.
PCI Express is designed to replace older earlier versions such as PCI, PCI-X, and AGP.

PCI Express slots come in standard sizes ranging from x1 (smaller) to x16 (larger). Modern homeboards will normally allocate space for at least one PCI Express x16 interface to install a custom graphics card.
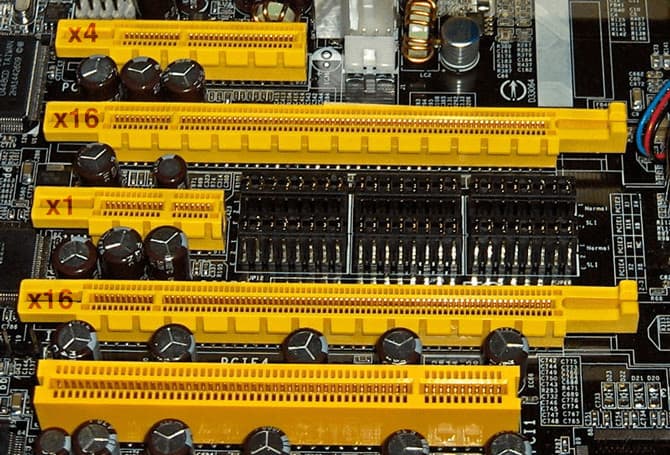
Smaller PCI Express slots, such as x1 or x4, are used for sound and network cards.
Read also:
Like most other panel slots, the incision on your edge connector will determine the direction of any of the components.
CMOS battery
The reason your computer can take off to your BIOS even if your operating system is down because bios is inside the CMOS chip. This CMOS chip is powered by a CMOS battery.
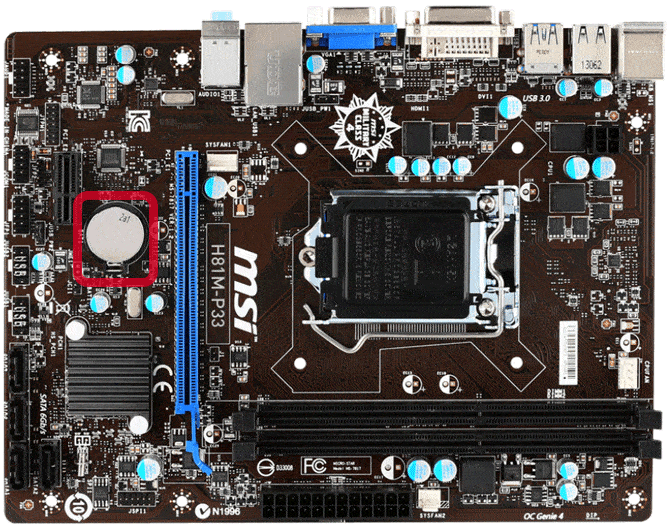
You may receive error messages regarding bios charging or suffer from some computer voltage-related problems, and you need to remove or replace the CMOS battery.
Just pull out the small lever on the battery side to remove the battery, which should appear immediately. Be careful with this element.
Power connectors
Power connectors are responsible for saving power to the motherboard via your power provider. With dedicated cables, they are called ATX connectors and provide a secure and consistent power connection to the motherboard.
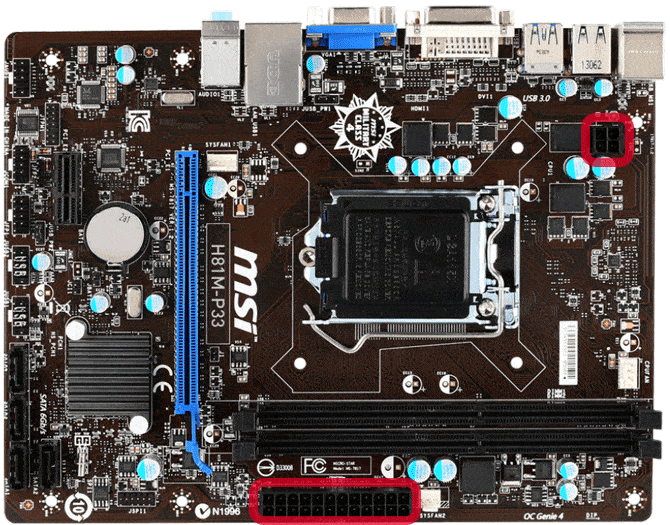
There are ATX connectors on the motherboard: one for the CPU and the other main connector for the rest of the board.
Front panel and USB connectors
There are power connectors for plug-ins for USB inlets, for example, in smaller groups. Front panel connectors can be a serious nuisance. For example, placing an error link in your power button connector causes the computer to fail.

When installing front panel connectors, be sure to spend your time and caution. You can also check your online user guide to find the order to install the precise front panel connectors of the motherboard.
SATA Connectors
SATA connectors allow users to connect their hard drive via the SATA cable.
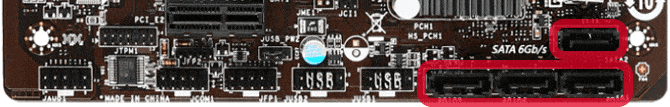
Read also:
The back panel
The backpanel provides users with a basic set of I/O connections such as LAN, USB, and audio port.
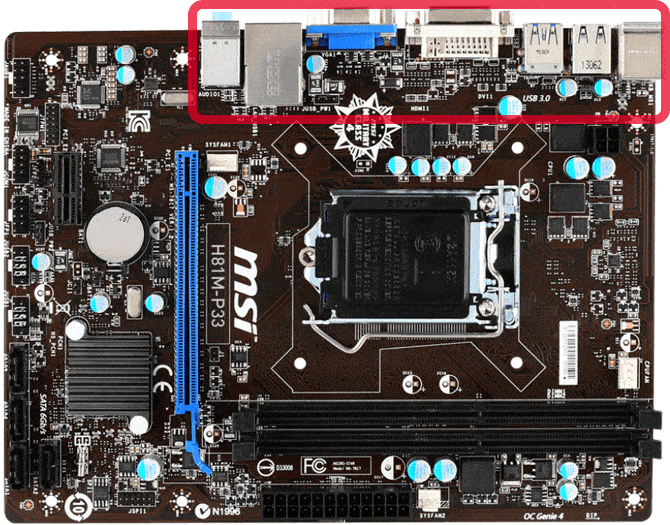
The image below shows a vertical layout of the H81-P33 background panel.

From left to right ports are: PS/2 ports for old keyboards and mouse mice (purple for the keyboard and green for mouse), USB ports 2.0 x, USB ports 3.0 x, DVI (white), VGA (blue) for screens, LAN port with additional USB ports below, and 3 x 3.5 mm audio port (light blue for microphone, light green for audio input, pink to output sound).
That’s (not exactly) everything!
Motherboard is a complex piece. The combinations of combinations and components are large and numerous. But now that you’ve learned the basics, open your PC and check to see if you can locate all of the above components on your motherboard. Who knows, it can be useful if you need to replace a component.
Are there any other ingredients you’d like to explain? Let us know in the comments below!





إترك رد